Hybridization- Steps, Types of hybridization
HYBRIDIZATION
Definition:
Hybridization is the method of producing new crop varieties
in which two or more plants of unlike genetically constitution all crossed together
that result in a progeny called hybrid.
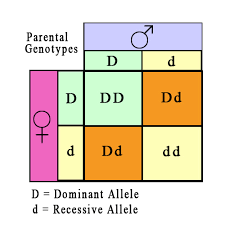
Hybridization offers improvement in crop and is the only effective means of combining together the desirable characters of two or more varieties or species. The first natural hybridization was observed by Cotton Mather in maize.
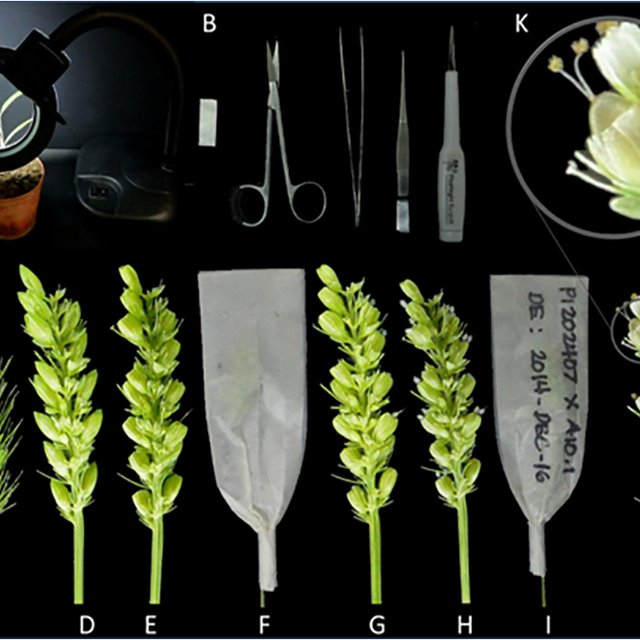
Steps in Hybridization:
1.Selection of Parents:
Male and female plants of the desired characters are selected. It should be tested for their homozygosity.
2. Emasculation:
It is a process of removal of anthers to prevent self pollination before dehiscence of anther
3. Bagging:
The stigma of the flower is protected against any undesirable pollen grains, by covering it with a bag .
4. Crossing:
Transfer of pollen grains from selected male flower to the stigma of the female emasculated flower.
5. Harvesting seeds and raising plants:
The pollination leads to fertilization and finally seed formation takes place. The seeds are grown into new generation which are called hybrids.
Types of Hybridization
According to the relationship between plants, the
hybridization is divided into.
i. Intra varietal hybridization -
The cross between the plants of same variety. Such crosses are useful only in self-pollinated crops.
ii. Inter varietal hybridization -
The cross between the plants belonging to two different varieties of the same species and is also known as intraspecific hybridization. This technique has been the basis of improving self-pollinated as well as cross pollinated crops.
iii. Inter specific hybridization -
The cross between the plants belonging to different species belonging to the same genus is also called intragenic hybridization. It is commonly used for transferring the genes of disease, insect, pest and drought resistance from one species to another. Example: Gossypium hirsutum x Gossypium arboreum – Deviraj.
iv. Intergeneric hybridization –
The crosses are made between the plants belonging to two different genera. The disadvantages are hybrid sterility, time consuming and expensive procedure. Example: Raphanobrassica, Triticale.











Comments