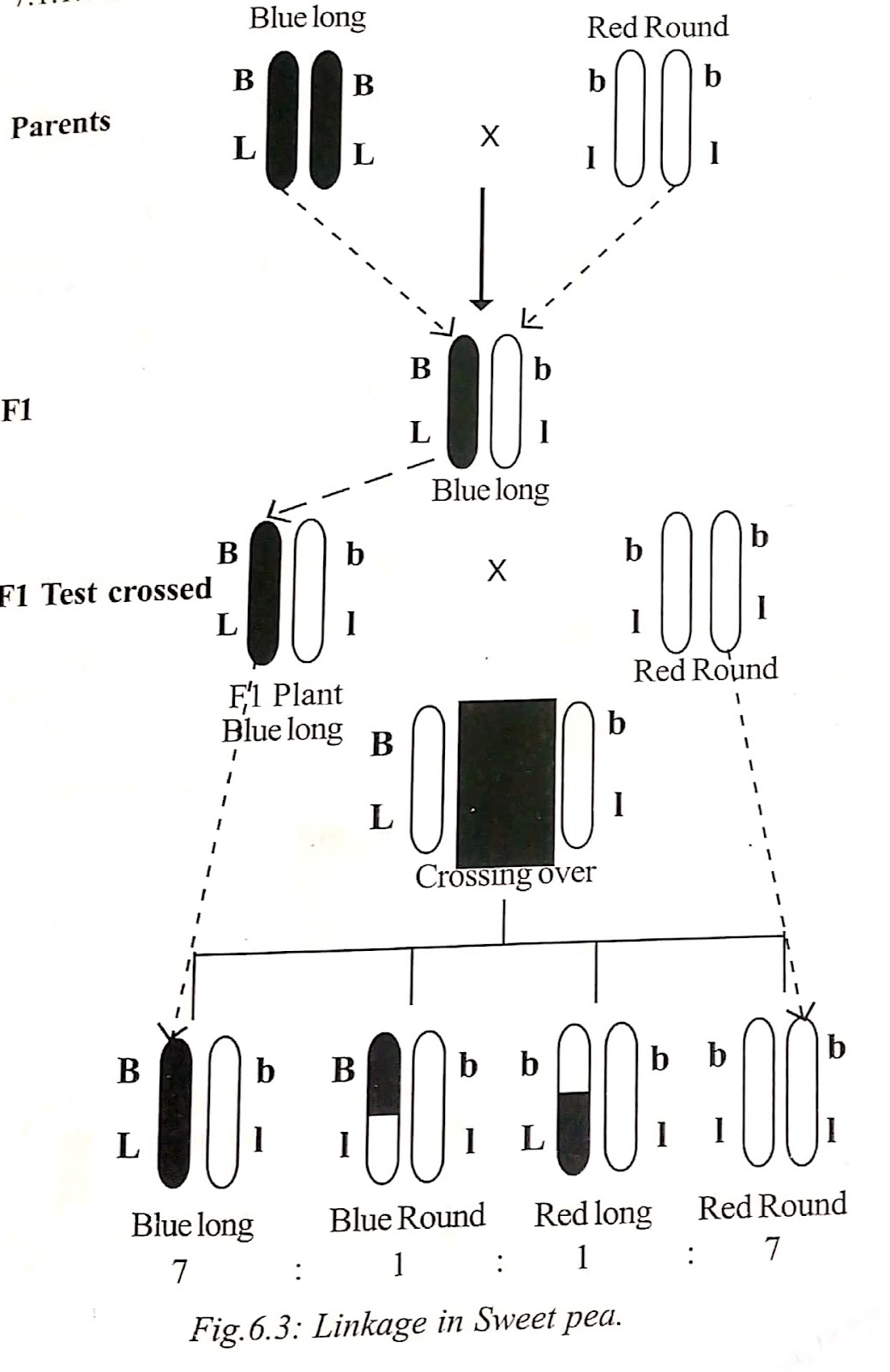
Linkage in Sweet Pea
Linkage in Sweet Pea
Bateson and Punnet (1906) studied linkage in sweet pea (Lathyrus
odoratus). In sweet pea, blue flower colour is dominant (BB) over red
flower (bb). Long pollen grain is dominant (LL) over round pollen grain(ll).
They crossed blue flowered, long pollen sweet pea with red
flowered, round pollen plant. In these plants, the genes for flower colour and
pollen shape are located in the same chromosome. That is, they are linked. The
linked genotypes of the parents are written as follows:
Blue flowered long pollen grained plant - BL/BL
Red flowered round pollen grained plant-bl/bl
The F1 plants were blue flowered with long pollen. The genotype
is written as BL/bl.
The F1 plant (BbLI) was test crossed with double recessive
plant (bl/bl). In the F2 generation, the plants appeared in the ratio 7:1:1:7
instead of the Mendelian test cross ratio 1:1:1:1.
Blue long-7
Blue round-1
Red long-1
Red round-7
It is a deviation of Mendel's dihybrid test cross. In the F2
the dominant alleles as well as the recessive alleles inherited together. Hence
the parent like plants are more i.e 14 out of 16. The parental combinations are
due to linkage. The new combinations are less just 2 out of 16. The new combi
nations are due to crossing over. In the same sweet pea plant, Bateson and
Punnet conducted another experiment. They crossed blue flowered round pollen
grained pea plant with red flowered long pollen grained plant. All the F1
plants were blue long. When they are test crossed with red round, in the F2,
the pea plants appeared in the ratio of 1 Blue long: 7 Blue round: 7 Red long:
1Red round.
In this experiment also, the parental combinations are more. ie, 14 out of 16. This means that the parental genes are linked together.


Comments