Sex Linked Inheritance - types, X linked, Y linked, XY linked, Completely sex linked and Incompletely sex linked inheritance , cris-cross/ zig zag inheritance
Sex Linked Inheritance
The transmission of body characters from parents to offspring
along with a sex is called sex linked inheritance. It is also called sex
linkage. The genes controlling body characters located on the sex chromosomes
are called sex linked genes. The body characters (other than sex characters)
controlled by genes located on the sex chromosomes are called sex-linked
characters. Sex linked inheritance was discovered by T.H. Morgan in 1910. The
following are the common examples for sex-linked inheritance:
1. Colour blindness
2. Haemophilia
3. Eye colour in Drosophila
4. Hypertrichosis (Hair in the ear pinna)
5. Ichthyosis hystrix.
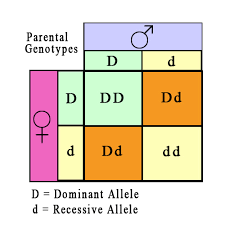
The sex linked genes are located on X chromosome or Y chromosome or both X and Y chromosome. The genes, controlling body characters, located on X chromosome are called X-linked genes. The inheritance of X-linked genes is called X-linked inheritance. The characters controlled by X- linked genes are called X-linked characters. Eg. Haemophilia, colour blindness, eye colour in Drosophila. The genes controlling body characters located on Y chromo- some are called Y-linked genes. The inheritance of Y-linked genes is called Y-linked inheritance. The characters controlled by Y- linked genes are called Y-linked characters. Eg. Hypertrichosis (hair in the pinna), Ichthyosis hystrix (scales on the body). The genes controlling body characters located on both X and Y chromosomes are called XY linked genes. The inheritance of XY linked genes is called XY linked inheritance. The characters controlled by XY linked genes are called XY linked inheritance. E Xeroderma pigmentosum, Retinitis pigmentosa, nephritis, etc. Most of the sex linked characters are recessive. They are more common in man than in woman. Most of the sex linked genes follow criss-cross inheritance (zig-zag inheritance). The inheritance of a character from the father to his grandson through his daughter is called criss-cross inheritance. That is, the sex linked character appears only in alternate generations.
Cris-Cross or Zig-Zag Inheritance:
The transmission of eye colour genes (the white eye colour
gene w) is in a specific pattern. It is transmitted from the father to his
grandsons through his daughters and never to or through his sons. This type of
transmission of genes from father to grandson through daughter is called
cris-cross or zig-zag inheritance.
Types of Sex Linked Inheritance:
There are five types of sex linked inheritance. They are as
follows:
1. X linked inheritance
2. Y linked inheritance
3. XY linked inheritance
4. Completely sex linked inheritance and
5. Incompletely sex linked inheritance.
1. X linked inheritance:
Certain sex linked genes are located only on X chromosomes and their alleles are absent from Y chromosome. These genes are called X linked genes; the characters controlled by these genes are called X linked characters and their mode of inheritance is called X linked inheritance. Eg. Colour blindness, haemophilia, eye-colour in Drosophila, etc.
2. Y linked inheritance:
The sex linked genes located on Y chromosomes only are
called Y linked genes. The Y linked genes are confined to males only. Hence
they are also called holandric genes (Holos-whole; andros- male). These genes
are transmitted directly from the father to the son. Their mode of inheritance
is called Y linked inheritance. Eg. Hypertrichosis, Ichthyosis hystrix, etc. Hypertrichosis
is characterized by the presence of tufts of hairs in the pinna. It occurs in
man only. Ichthyosis hystrix is characterized by the presence of scales on the
body.
3. XY linked inheritance:
Certain sex linked
genes are located on both X and Y chromosomes. They are called XY linked genes
and their mode of inheritance is called XY linked inheritance. Eg. Xeroderm
pigmentosum, nephritis, retinitis pigmentosa, etc.
4. Completely sex linked inheritance:
The X and Y chromosomes are not similar. The X chromosome is
larger and straight. But the Y chromosome is smaller and one end is curved. The
lower part of X chromosome is similar to that of Y chromosome. These two parts
are called homologous regions. They have the same type of genes. The remaining
parts of the X and Y chromosomes are not similar. So they are called
non-homologous regions or differential regions. They do not contain similar
type of genes. The genes located on non-homologous regions inherit together
because crossing over does not occur in these regions. So the genes located on
non-homologous regions are called completely sex linked genes and their
inheritance is called completely sex linked inheritance. Eg. Haemophilia,
colour blindness, etc.
5. Incompletely sex linked inheritance:
The genes located on homologous regions of sex chromosomes do not inherit together because crossing over may occur in these regions. So these genes are called incompletely sex linked gene and their mode of inheritance is called incompletely sex linked in heritance. Eg. Retinitis pigmentosa, nephritis, etc.



Comments